Articles
What is HTTP Protocol?
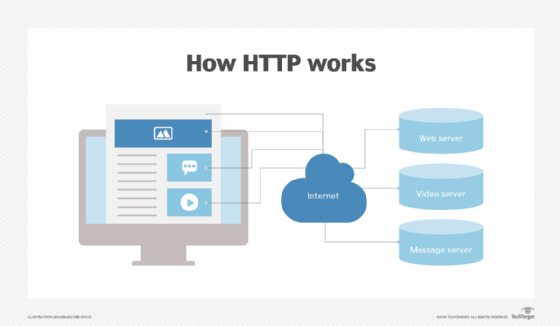
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, and it’s the foundation of the web we know today. It’s a set of rules that govern how web servers and browsers communicate with each other to send and receive information.
To understand how HTTP works, let’s consider a simple example. Imagine you want to visit a website, so you type its URL into your browser and hit enter. Your browser sends an HTTP request to the server hosting the website, asking it to send the webpage back to you.
The server receives the request and responds by sending an HTTP response back to your browser. This response includes the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript that make up the webpage, as well as other resources like images and videos. Your browser then uses this information to render the webpage on your screen.
HTTP is a stateless protocol, which means that the server doesn’t store any information about the client’s session. Each request is treated as a separate, standalone event. This is in contrast to protocols like FTP (File Transfer Protocol) or SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), which maintain a connection between the client and server for the duration of the session.
One of the key features of HTTP is that it’s based on a request-response model. The client (usually a browser) makes a request, and the server responds with a response. There are several types of HTTP requests that a client can make, including GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE.
GET requests are used to retrieve information from the server. For example, when you visit a webpage, your browser sends a GET request to the server to retrieve the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript that make up the webpage.
POST requests are used to send data to the server, usually as part of a form submission. For example, when you fill out a form on a website and click “submit,” your browser sends a POST request to the server with the form data.
PUT requests are used to update a resource on the server. For example, you might use a PUT request to update the information in a database record.
DELETE requests are used to delete a resource on the server.
HTTP is a crucial part of the internet, and it’s what enables us to access and share information online. Without it, the web as we know it wouldn’t exist.
In addition to the request types mentioned above, there are also several HTTP response codes that a server can send back to the client. These codes indicate the status of the request and whether or not it was successful.
Some common HTTP response codes include:
- 200 OK: The request was successful and the server was able to fulfill it.
- 301 Moved Permanently: The requested resource has been moved to a new URL, and the server sends this response code along with the new URL.
- 404 Not Found: The requested resource could not be found on the server.
- 500 Internal Server Error: An error occurred on the server while processing the request.
HTTP is an important part of how the web works, and it’s something that most of us use every day without even thinking about it. Whether we’re visiting a website, filling out a form, or uploading a file, we rely on HTTP to send and receive information.
It’s worth noting that HTTP is just one of many protocols that make up the internet. Others include TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), which is the underlying protocol that enables the communication between computers on the internet, and SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security), which is used to encrypt communication between a client and server.
Find an overview of HTTP Protocol here. and additional information on HTTP protocol here.
In conclusion, HTTP is a vital part of the internet, and it’s what enables us to access and share information online. Whether we’re browsing the web, filling out a form, or uploading a file, we rely on HTTP to communicate with servers and other clients.
Guest Post
Beat Recession Blues with These PHP Web Development Best Practices

With the recession taking over the majority of economies across the globe, securing your job has become the topmost priority. The scenario is the same across different verticals and for programmers, it is even worse. As the resource pool of PHP developers is expanding, the crunch of right projects and jobs is also deepening. Organizations are paying emphasis on quality rather than quantity. It’s all about the survival of the fittest.
Getting your hands on a handsomely paying project is not just a matter of luck. It also readily depends on the quality of services rendered by you as a developer. A PHP web development project requires you to have in-depth knowledge of the language and deploy industry best practices. As you scan your clientele in hope of grabbing onto the next breakthrough project, here are some coding best practices that can get you through the stringent quality evaluations of even the daintiest clients:
- Get Friendly with Single Quoted Strings: Using single quotes over double quotes gives you a marginal performance benefit, especially if you are coding some intricate project. A PHP string that is surrounded in double quotes is misinterpreted as variables and special characters by the PHP interpreter. If you want a single-string output, it is best to use single quotes. It enhances the performance of your PHP application as the string doesn’t get parsed.
- Don’t Use Regular Expressions Unnecessarily: Keep a safe distance from ereg and preg function groups as and when possible, especially if you are performing basic string operations. When str_replace and strtr functions are faster than preg_replace, why do you wish to stick with old school functions? Move on and save your application from those crunch cycles.
- Short Open Tags are a Big No-No: Are you still torturing your PHP application with short tags? It’s time you show some mercy. <? Is just a bad code form and creates conflict with XML parsers. It will also annoy people who will try modifying your code in PHP directives. So, you won’t find even a single justification for using open tags. Use full tags instead and let your application breathe.
- Keep Functions out of Loop Declarations: Using functions inside loops is not a great idea. It is annoying to see how some developers stake the performance of the application to save an extra line of code. If you use a function inside a loop, it will get executed as and when iteration initiates. If you have a bigger loop, this will mean you are increasing the execution time, which is not a bit user-friendly.
- Document Your Code: You might have heard it a hundred times, but it by no means depreciates its value. Documenting your code means you value your hard work as well as your client’s investment in the programming phase. Many organizations will hire you just on the basis of your documentation habits.
- Variable Initialization is a Must: If you don’t initialize a variable, PHP will create it automatically, but it is best not to rely on this feature. The code becomes sloppy and God forbids if you have to track down the initiating point of the variable, you will have to scan through the entire code. Moreover, incrementing of an uninitialized variable takes more time than that of an initialized variable. So, it’s best to initialize a variable.
PHP web development can be a tricky job, especially when so many others are keeping a watch, waiting to grab any opportunity that comes their way. It is best to follow best practices and adhere to stringent quality standards, to rapidly increase your client base.
Author:- Steve Graham is an expert in PHP Web Development, who has been blogging on the niche for the last 6 years. Currently, he is associated as a freelancer with a PHP development firm that deals in PHP Development Outsourcing.
Guest Post
The Best Christmas Apps for iPhone 5

The Christmas spirit is often one that takes a little while to get into, however, iOS devices and the Apple store have your back with a range of amazing Christmas apps that will put you in the mood for the holidays and put the happiness back in your heart.
Fortunately, Christmas usually coincides with the arrival of a new phone, meaning many of us will have the new iPhone 5 for Christmas apps. So, what are the best fun iPhone apps available for Christmas?
Blabber Box – Christmas Edition
There’s nothing like a bit of a laugh to lighten up proceedings and the good people at blabber box have provided a giggle or two with the Blabber Box Christmas Edition. Choose from one of four characters and then record and animate your vocals over some half-minute cartoons of Santa, a nutcracker, Rudolf, and of course an elf. It’s silly fun, but a great way to lift those Christmas blues.
Christmas Fire
Chestnuts roasting on an open fire – it sounds idyllic, doesn’t it? Unfortunately, many of us don’t have the liberty of an open fire at Christmas. However, for those who fall into the aforementioned category, there is an answer – Christmas Fire from the App Store. The app creates the crackle of a fire and even has a number of Christmas tracks included. The perfect alternative to the Christmas fire – well, maybe not, but cool nonetheless.
White Christmas
We all dream of a white Christmas and with this app, you can have it. The live photo-taking app will create the effect of snowfall on your iPhone, allowing you to create a snowy Facebook profile photo. There’s also the option to add Santa and a number of other festive templates to the image. It also uploads directly to social media.
Santa GPS
If you have little ones then you will certainly have to await the excitement of Christmas with eagerness. Of course, it can be hard to know how Santa is doing and where he is. Fortunately, there is an answer with the Santa GPS. This app shows you where the man himself is on the night in question. The app even has a Good and Naughty list that allows you to check your position.
oChristmas Tree
This app really encapsulates the feeling of Christmas. From the crackling fire to the snow falling outside, this app has it all and even allows you to choose from up to 63 ornaments for your tree. These also include a range of animations and sound effects with ornaments and you can then send your tree with festive lighting and all to friends and family.
Festive Holiday Baking
Christmas is about food and this festive app has a wide range of great baking recipes that are made with less than 8 ingredients – most of which you will have. It’s a nicely laid out app that will provide a festive feel for your stomach.
Christmas Music
This app has over 10,000 free songs for you to play throughout Christmas and with this sheer number, we would say you can play without repeat from November to January.
Christmas apps are a great way to get into the spirit of things, so why not download a few and have some fun?
Cormac Reynolds writes for Festive-lighting.com a UK-based company that supplies all your decoration needs for the festive season.
Guest Post
5 Unique Business Card Designs Your Clients Will Love

Business cards are an excellent way to share your information, especially if you’re self-employed. The only problem is that business cards can be boring. The key to surviving in today’s world is standing out, even when passing out business cards. This means thinking outside the box with a business card that makes it easy to remember. The following are just five unique business card designs your clients will love.
Multipurpose Cards
When giving out a business card, why not give customers something they can use. For example, your business card may serve as a ruler or ice scraper for your car. It’s best to match your multipurpose business card to your business. A bookstore owner may have business cards that serve as bookmarks or an illuminated business card for nighttime reading.
Edible and Drinkable Cards
It doesn’t matter what type of business you’re in, edible and drinkable business cards will get you noticed. You might have business cards that have teabags attached or have a bakery make cookies with your business information. These would be great for conventions.
Comb Cards
Those running a hair salon or beauty supply store should definitely consider comb cards. These are just what they sound like, a plastic business card that features a comb on one side. It’s unique and something that customers can throw into their purses. Remember, when business cards are useful, they’re more likely to get noticed rather than tossed in a drawer.
Dog Tag Cards
Dog tag business cards are something that stores that cater to men should definitely look into. It’s something that men are going to find truly unique and memorable. For example, those that run a gun and ammo shop or a shooting range would greatly benefit from this style of card.
Map Card
Want more people to find your business, then make it easy for them to do with your business card. There are business cards that unfold into a map or those that feature a map on the back. Remember, you want something that is unique. You might even have the map drawn out on cookie business cards. Now that would be memorable.
Business cards don’t have to be the same old thing. Unfortunately, even cute designs are getting old. With more and more people working for themselves, you need to stand out and a regular business card won’t get the job done. That’s why you need to design a unique business card. Whether it’s an edible card or even a comb, this is something that should be memorable to your customers.
About the Author: Marlin Morrisroe loves finding unique ways to market his business. Cookies, anyone?
-
Tips & Tricks2 weeks ago
WordPress Security Hacks
-

 Pages3 months ago
Pages3 months agoWrite For Us – Guest Post
-
Showcase3 months ago
StylizedWeb.com
-
News3 months ago
How to: Show/Hide any div box with jQuery in WordPress
-
Tips & Tricks2 months ago
Remove the title attribute using jQuery
-
Tips & Tricks7 months ago
How to: show/hide a widget in WordPress with jQuery
-

 Plugins7 months ago
Plugins7 months agoTop Membership plugins
-
Tips & Tricks3 months ago
Limit the characters that display on the_title










